Islamic Sharia is a regulation regarding all matters related to Islamic laws and regulations. Including in terms of the economy in Indonesia. Because the majority of the Indonesian population is Muslim, there is a Sharia Economy applied in our country. This time, we will discuss what Sharia Economics is. Sharia economics is a form of branching of economics based on Islamic values. These values are based on the Qur'an, Sunnah, Ijma', and Qiyas. For more details about this sharia economy, you can understand it through the following explanations.
Sharia Economics Is
The sharia economic system is a system based on a market economy where goods and services are freely exchanged based on demand and supply. You can use money or barter or debit and credit values. In addition, in this system, entrepreneurs are also encouraged to create rich jobs and also social activities. Actually, it can be said that the Islamic or sharia economic system is a system that balances between the two systems. It emphasizes economic freedom and also the need to serve the common good Based on this, especially from the economic system number 3 which is based on sharia or Islamic law, several questions arise, how the economy and religion can be combined. In this case, we must understand that the economic system is a man-made system that functions to regulate and also to reform trade. Efficacy, growth, freedom and also equity are the main goals to get a good economic system condition. Why the Islamic economic system? To understand this, let's find out about the Islamic world.
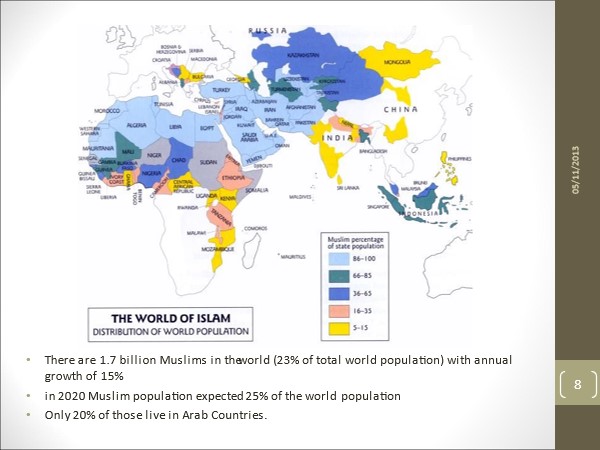
From there, we learn what the definition and interpretation are in sharia law. Sharia law is the values that underlie the entire Islamic way of life. Shari'a will give guidance to those who believe in it about what is halal and what is not allowed and acceptable behavior in all areas of Muslim life. Sharia is an Islamic teaching developed by several scholars, namely Shafii, Hambali, Hanafi and Maliki, almost 1000 years ago, or almost 400 years after Islam was revealed and taught by the Prophet Muhammad. The main concept of sharia law is that it is permissible, or every business activity is allowed, except for those that are prohibited. The sharia economic system is based on Sharia law consisting of the Qur'an, Sunnah, Ijma, Ijtihad or reason and Qiyas or analogy.
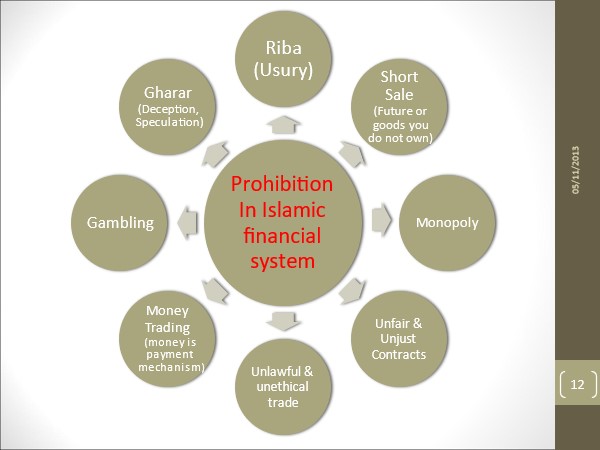
The Islamic economic and financial system is a concept that can be applied not only to Muslims, but also to other people who follow and want to join the concept. There are several reasons for that. The first is the use of the concept of risk sharing. In this world, it is applied in the division of profits and losses. In Indonesia we use the concept of profit sharing. In the sharia economic system, money is used as a medium of transactions but not as a commodity. This system is prohibited from riba, but we must understand that there are alternative systems that do not use usury. Because there is a prohibition from gharar, such as the capital market for short sell transactions, transactions in the sharia economic system must be transparent and also free from fraud. The Islamic economy has experienced rapid development in the last two decades. The main influencing factor is the increase in the number of Muslim populations which will reach 27.5% of the world's population by 2030. Furthermore, it will increase the demand for halal products and services. In 2016, the total size of global Islamic financial assets reached $2.2 trillion and is projected to grow by nearly 72% to $3.78 trillion in 2022. Islamic bank assets had a significant growth of around 1.5% globally in 2018-2019 while conventional banks lagged behind at 1%. Indonesia's sharia economic market still lags behind other OIC countries in terms of outstanding Sukuk (sharia bonds) and managed sharia funds (AuM), even though Indonesia is the largest Muslim country in the world, where it will contribute 12%. of 23% of the Muslim population globally in 2022. There is room for the growth of Sharia businesses, such as payments, loans, credit cards, investments, bond insurance, and other services.
Sharia Economic Law
The Islamic economic system is an economic system that is sourced from the Qur'an and As-Sunnah related to economic affairs. Islamic economics can be used as a solution to solve economic problems that plague the world. In contrast to Western economies, the approach is based only on materialistic calculations, profit and loss, without religious moral content. Although Halide's thinking is still normative-deductive, at the level of scientific discourse, the idea of Islamic economics has entered the scientific realm and has become the basis for the development of Islamic economics at the practical-operational level. Various general economic policies issued by the New Order government in the period 1967-1991 include: (1) Foreign Investment (PMA) and Domestic Investment (PMDN) Policy in 1967, (2) First Five-Year Development Plan (1969), (3) Second Five-Year Development Plan (1974), (4) Third Five-Year Development Plan (1979), (5) Third Five-Year Development Plan (1984), (6) The Fourth Five-Year Development Plan (1989), the PMA and PMDN policies are intended to attract as much as possible private participation, both private and foreign, and domestic, to grow the business world as a solution to overcome the crisis. Macro-wise, the Islamic economy experienced rapid development and progress after the establishment of the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) in Jeddah in 1975. This is able to attract attention and influence the mind map of global financial practices. Islamic economic discourse and practice have an appeal among academics, professionals, and economic practitioners both at the national and international levels. The study of Islamic economics and finance continues to grow both in Muslim countries and in Europe. In Indonesia, the emergence of the Islamic economy was marked by Bank Muamalat in 1992, based on Law Number 7 of 1992. Although Islamic economic problems are relatively late in coming, the enthusiasm of Muslims to learn about them is very strong. The study of Islamic economics in various seminar forums, discussions run dynamically by involving various universities, both public and private, both universities owned by Muslims and non-Muslims. Islamic financial institutions have been overgrown since 2000 until now spread throughout the province. The growth of Baitulmal wa Tamwil (BMT) as an institution engaged in sharia microfinance services until 2010 reached 1,400 BMT spread throughout Indonesia. Likewise with the massive development of Islamic banking. In addition, there are also interesting developments related to the birth of Islamic banks in the framework of a dual banking system (Fathurrahman, 2010). In 2013, Indonesia's banking growth represented $1.7 trillion in assets, growing 17.6 percent. The development of Islamic finance has large assets that will continue to experience greater growth than conventional finance in the future (Azma et al., 2018). According to Ma'ruf Amin as the vice president of the Republic of Indonesia and former Chairman of DSN-MUI, at the Seminar on the Preparation of Nash and Hujjah Sharia Sharia Economics on July 11-12, 2006 stated that the presence of Sharia economy in Indonesia is growing rapidly, marked by the growth of Islamic financial institutions spread throughout Indonesia. A new form of bank has emerged in the middle of the 20th century that carries a set of principles, characteristics and objectives that distinguish it from existing conventional banks such as Sharia banks, which rests on a clear philosophy, namely adherence to the teachings of tolerant Islam. Islamic banks have adopted a new banking system that distinguishes them from other banks that rely on the concept of usury interest. Their activities involve collecting or creating pools of funds from various sources and investing them in accordance with Islamic Sharia (Maswedah, 2020). The risk of macro conditions is certainly influenced by the concept of Islamic business. First, the basic concept of sharia business is that it must be fair, balanced, and mashlahat. Second, the concept of sharia business must be fair because of the principle of profit sharing (Muafi et al., 2020). In addition, the position of sharia in Indonesia is getting stronger marked by the birth of Law number 10 of 1998 concerning amendments to Law number 7 of 1992 concerning Banking. This law recognizes the dual banking system in Indonesia as conventional and the sharia system. In addition, Law Number 3 of 2006 concerning Amendments to Law Number 7 of 1998 concerning Religious Courts, which expands the authority of Religious Courts to resolve cases related to the sharia economy. The fatwa of the National Sharia Council is also the operational basis of Islamic financial institutions; However, it does not have binding force, only as a legal consideration of the judge in his decision. The authority of the Religious Court is as per Law number 3 of 2006 concerning the Settlement of Sharia Economic Disputes which requires the presence of KHES based on PERMA Number 2 of 2008, September 10, 2008, as a strict guideline and handle for Religious Court Judges to avoid disparities in the judges' decisions. This means that the legislation of sharia economic law in Indonesia is very strategic in encouraging national economic growth (Yasin, 2016).
Principles of Sharia Economics


 Last:
Last: 







